The humoral arm of innate immunity consists of numerous pattern recognition molecules, such as mannose-binding lectin (MBL) and pentraxin 3 (PTX3).
Humoral pattern recognition molecules persist as the ancestors of antibodies deployed in adaptive immune response, recognizing pathogens and eliminating them by a diverse range of mechanisms.
Generally, they bind with virus envelope glycoproteins, as has been observed in influenza, hepatitis C, and herpes simplex virus, inducing one of the several elimination routes available or directly preventing interaction with host cell membranes.
The most severe symptoms of COVID-19 are associated with an over-response of the cellular innate immune system, where a signaling cascade induces a cytokine storm, and our understanding of this aspect of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection has advanced considerably since the early stages of the pandemic.
There has, however, been less investigation into the role of the humoral arm of the innate immune system.
In a paper recently uploaded to the preprint server medRxiv* by Garlanda et al. (June 8th, 2021), humoral pattern recognition molecules are explored for affinity towards SARS-CoV-2, contributing to unraveling the role of these molecules in COVID-19 disease progression.
.jpg)
Identifying relevant pattern recognition molecules
A solid-phase binding assay was utilized to investigate any interaction between the ten selected humoral innate immunity molecules and SARS-CoV-2 proteins, specifically the: spike protein trimer, S1 and S2 subunits of the spike protein, nucleocapsid, and envelope proteins. Protein Coding gene PTX3 was seen to bind in a concentration-dependent manner to the nucleocapsid protein, and as this is a large glycoprotein with distinct C- and N-terminal domains, each domain was also tested against the nucleocapsid protein, finding that the N-terminal domain was the main contributor, though bound more weakly than the full-length protein.
Instead of the nucleocapsid, MBL was observed to bind with the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, though not the separate subunits, possibly indicating that the closed form of the spike trimer is needed for interaction.
MBL is a member of the collectin family, bearing a Ca2+ type lectin domain, and so the group selected six additional molecules from this family for further analysis. None showed any affinity towards the spike protein compared with MBL, suggesting that the interaction is unique to this molecule and not due to the structural similarities shared by the collectin family.
The group modified a lentivirus vector to bear the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and exposed to MBL, demonstrating specific interaction between the pseudovirus particles and the pattern recognition molecule.
As discussed, pattern recognition molecules largely interact with glycans, which heavily coat the surface of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. The protein bears 22 N-glycosylation sites, 8 of which contain oligomannose-type glycans that are probable interaction sites with the MBL carbohydrate recognition domain. The group exposed the spike protein to D-mannose or N-acetyl-glucosamine before MBL, finding that binding was now inhibited, and confirming the Ca2+ dependent pathway. The group searched the molecule for suitable binding sites, selecting for those with high oligomannosylation occupancy, and eventually identified two probable sites that span the S1 and S2 subunits, explaining the lack of interaction with them individually. The spike proteins of variants of concern B.1.1.7, B.1.1.28, and B.1.351 were also analyzed in silico for changes in possible binding sites with MBL, with the mutations not appearing to significantly alter the glycosylation sites. Docking simulations and in vitro testing using variant of concern spike proteins confirmed that MBL binds with an equal affinity towards wildtype and later lineages of SARS-CoV-2.
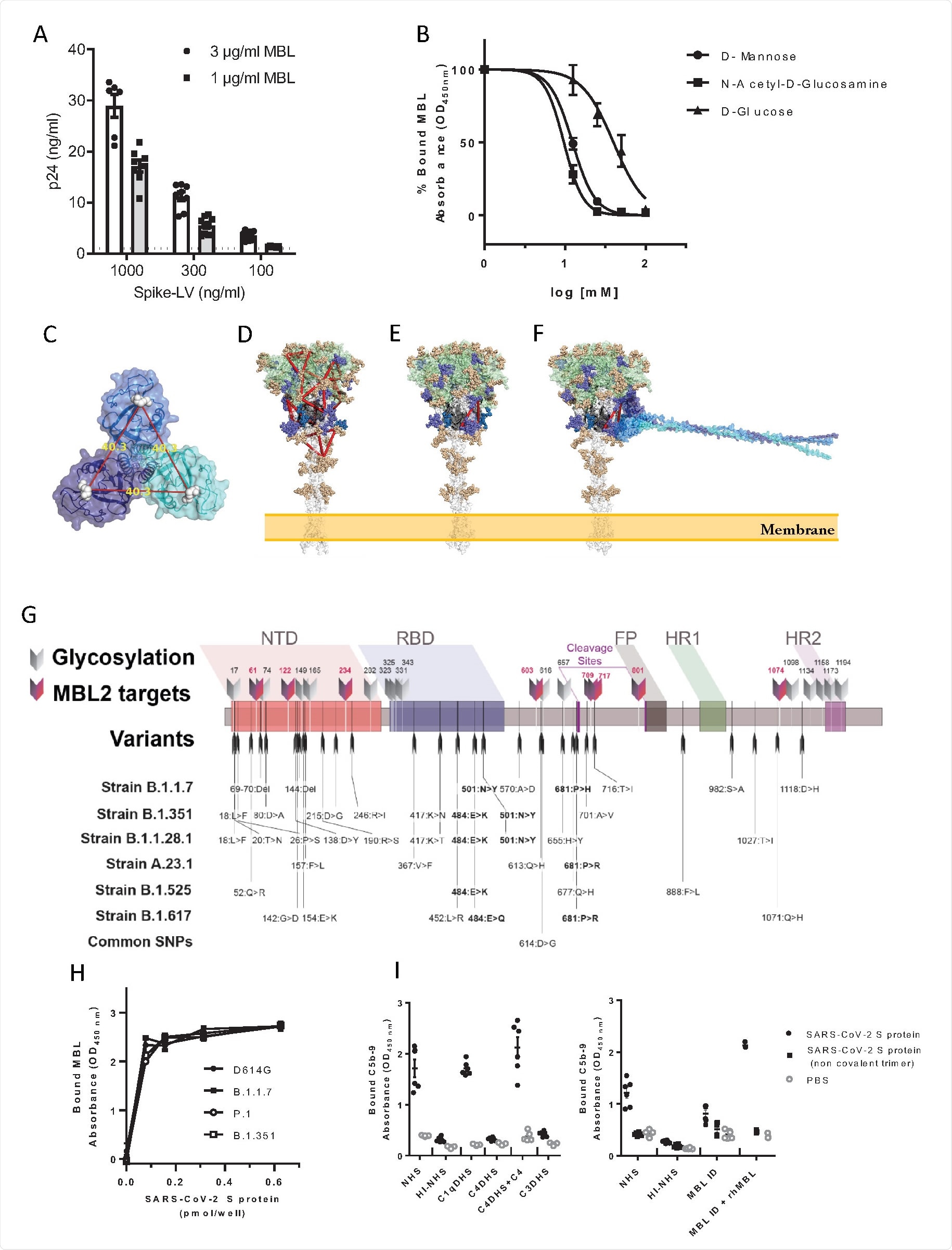
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2
To further test whether MBL inhibited cell entry by SARS-CoV-2, the spike protein-bearing lentiviral vectors were applied to Calu-3 cells and 293T cells heavily expressing the ACE2 receptor, with the pattern recognition molecule present at varying concentrations. At the highest tested concentration of 34 nM viral cell entry was inhibited by 90% in 293T cells, with an EC50 of around 1.7 nM. Calu-3 cells are lung-derived epithelial cells, and thus more relevant to the investigation of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors, and against these cells, the calculated EC50 was just 0.27 nM at 72 hours post-infection.
MBL and PTX3 were also applied to a 3D human bronchial epithelial cell model, finding that the former was able to decrease viral production by an order of magnitude when applied at a concentration of 170 nM by 72 hours post-infection. The production of interleukin-8 and other key inflammatory cytokines was also inhibited by MBL, though presumably due to the lower rate of infection in tissues treated with the molecule.
Finally, the group performed data analysis of Italian COVID-19 patients where data regarding genetic variation in the MBL producing gene was available. One polymorphism, in particular, was highlighted as being associated with increased susceptibility to COVID-19 infection and more severe symptoms, which has also been implicated with a poorer prognosis in influenza and other respiratory infections.
The group suggests that recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by MBL could play both a positive and negative role in disease progression, as it serves as a form of antiviral in the early stages of infection, though it may then exacerbate the inflammatory response observed later in severe cases.
*Important Notice
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
- Recognition and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by humoral innate immunity pattern recognition molecules, Matteo Stravalaci, Isabel Pagani, Elvezia Maria Paraboschi, Mattia Pedotti, Andrea Doni, Francesco Scavello, Sarah N. Mapelli, Marina Sironi, Luca Varani, Milos Matkovic, Andrea Cavalli, Daniela Cesana, Pierangela Gallina, Nicoletta Pedemonte, Valeria Capurro, Nicola Clementi, Nicasio Mancini, Pietro Invernizzi, Rino Rappuoli, Stefano Duga, Barbara Bottazzi, Mariagrazia Uguccioni, Rosanna Asselta, Elisa Vicenzi, Alberto Mantovani, Cecilia Garlanda, medRxiv, 2021.06.07.21258350; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.07.21258350, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.06.07.21258350v1
Posted in: Medical Research News | Disease/Infection News
Tags: ACE2, Antibodies, Assay, Carbohydrate, Cell, Coronavirus, Coronavirus Disease COVID-19, Cytokine, Cytokines, Gene, Genetic, Glucosamine, Glucose, Glycans, Glycoprotein, Glycosylation, Hepatitis C, Herpes, Herpes Simplex, Herpes Simplex Virus, Immune Response, Immune System, in vitro, Influenza, Lentivirus, Molecule, Nucleotide, Pandemic, Protein, Pseudovirus, Receptor, Respiratory, SARS, SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Spike Protein, Syndrome, Virus

Written by
Michael Greenwood
Michael graduated from Manchester Metropolitan University with a B.Sc. in Chemistry in 2014, where he majored in organic, inorganic, physical and analytical chemistry. He is currently completing a Ph.D. on the design and production of gold nanoparticles able to act as multimodal anticancer agents, being both drug delivery platforms and radiation dose enhancers.
Source: Read Full Article