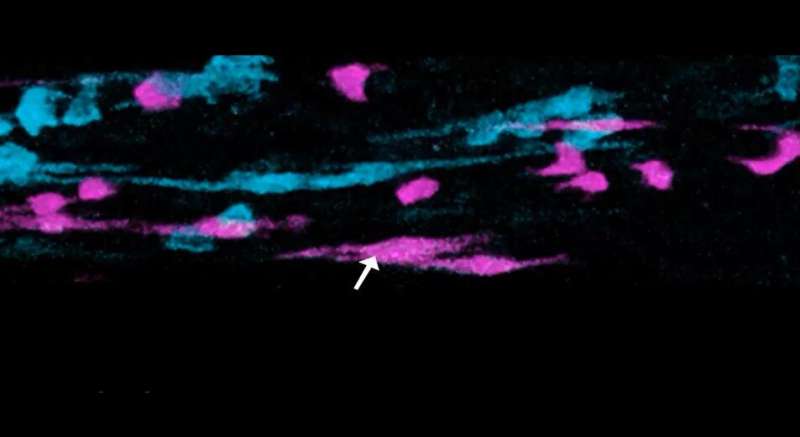
An improved high-tech fluorescence microscopy technique is allowing researchers to film cells inside the breast as never seen before.
This new protocol provides detailed instructions on how to capture hi-res movies of cell movement, division and cooperation, in hard-to-reach regions of breast tissue.
The technology—called multiphoton microscopy—uses infrared lasers to illuminate fluorescently labeled breast cells without harming them, so that elusive cell behaviors can be observed within living tissue.
With the new method, WEHI researchers have revealed how breast cells rearrange, interact and sense their environment as the breast grows during development and recedes after lactation.
Cell imaging within living tissue has been achieved in many organs but the breast has remained especially challenging. So far, this new method has revealed exciting and unexpected details of breast biology and will help teams worldwide to advance research on breast development and cancer.
Understanding cell function
The protocol was developed by researcher Dr. Caleb Dawson, in a team led by Professor Jane Visvader and Dr. Anne Rios, in collaboration with Dr. Scott Mueller from the Doherty Institute, and published in Nature Protocols today.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=LV_9V4saKrI%3Fcolor%3Dwhite
Dr. Dawson said the filming technique unlocked a variety of applications to better understand how cells function, interact and develop.
“One of the most valuable things we have been able to film with the technique are the terminal end buds (TEBs) in breast tissue,” he said.
“These are club-like structures at the tips of the mammary ducts that grow during puberty to produce the branched tree structure of breast tissue. The unique cells inside the TEBs have never been filmed like this before so it was fascinating to watch this process for the first time.”
“We have watched a cell behavior inside the TEB that was hypothesized in the 1980s but was never proven, and which has implications for breast stem cell function.”
Previously, TEBs had been studied by dissociating the individual cells and filming them outside the breast or by taking still images. With these approaches it is difficult to know how the cells actually behave and interact in living tissue.
“By filming the moving cells inside intact breast tissue in laboratory models, we are able to grasp a better understanding of how the cells behave and cooperate to help the breast to form and function properly.”
Dr. Dawson said that he was grateful for the brilliant team and the cutting-edge technology provided by the Center for Dynamic Imaging at WEHI that made this work possible.
“When we embarked on our mission to film these processes, I had little knowledge of the effort it would require. With the vision of leading breast researchers Professor Visvader, Dr. Rios and Professor Geoff Lindeman, alongside the live imaging expertise of Dr. Mueller, and the microscopes available, we were able to achieve something that very few labs in the world have accomplished,” he said.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Lle0v98L1JE%3Fcolor%3Dwhite
Opening the doors to new research opportunities
Dr. Dawson said the filming technique could be applied to a host of research endeavors.
“Our approach enables us to image up to six fluorescent colors at the same time, which allows us to see how more cell types interact,” he said.
“We can image different stages of breast development, immune cells, lymph nodes and hair follicles and watch how individually-labeled cells function.”
“This means we can create beautiful images with extremely fine details about the cell shapes to get a better understanding of how cells interact and change over time. This opens up many new research opportunities and we are only just starting to see the potential of what this could be used for.”
Dr. Dawson said he hoped the imaging protocol would make this type of imaging more widely accessible to researchers.
Source: Read Full Article