Editor’s note: Find the latest COVID-19 news and guidance in Medscape’s Coronavirus Resource Center.
New cases of COVID-19 dropped among children for just the second time in the past 6 weeks, but that was not enough to reverse the trend in children’s share of the weekly total, according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
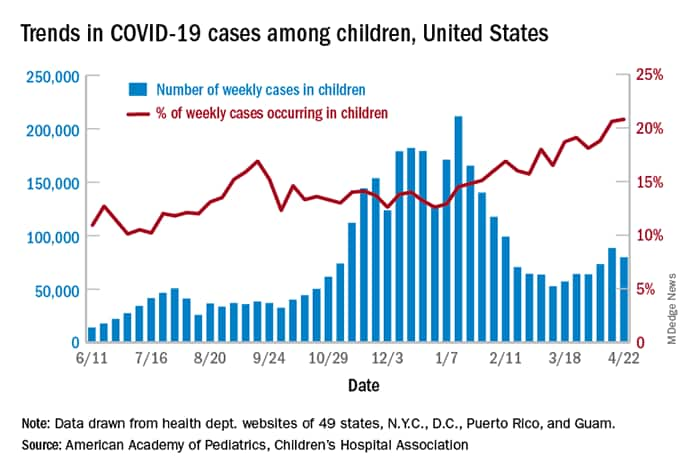
Despite the decline in new cases, which fell from 88,000 to just under 80,000, or 9.7%, during the week of April 16-22, children represented 20.8% of all COVID-19 cases reported for the week, surpassing the pandemic-high 20.6% seen just a week earlier, the AAP/CHA report shows.
The total number of cases in children is now over 3.7 million — that’s 13.7% of cases in all ages — since the start of the pandemic, and the cumulative rate of infection has reached 4,931 per 100,000 children, based on data from 49 states (excluding New York), the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
Cases of more severe illness in children continue to trend lower. The cumulative number of hospitalizations in children (15,187) is only 2.0% of the total of almost 760,000 in the 25 jurisdictions (24 states and New York City) that report such data, and deaths in children now number 296, which is just 0.06% of all COVID-19–related mortality in 43 states, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam, the AAP and CHA said in their report.
Among those 46 jurisdictions, Texas has reported the most deaths (51) in children, followed by Arizona (29) and New York City (23), while 9 states and the District of Columbia have reported no deaths so far. Children represent the highest proportion of deaths (0.19%) in Colorado, but Guam, with 2 child deaths among its total of 136, has by far the highest rate at 1.47%, the AAP/CHA data show.
Data from the 25 reporting jurisdictions show that children make up the largest share of hospitalizations (3.1%) in Colorado and Minnesota, while New York City (1.9%), Georgia (1.3%), and Rhode Island (1.3%) have the highest hospitalization rates among children diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infection, the two groups reported.
This article originally appeared on MDedge.com, part of the Medscape Professional Network.
Source: Read Full Article