Strict lockdowns have been implemented in many countries since the beginning of 2020 to limit morbidity and mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic. A COVID-19-related lockdown was first imposed in the UK in March 2020, and restrictions then eased from June and July onwards before implementing harsher restrictions at the beginning of October. Various forms of lockdowns with different timing and duration were enforced across the UK in November and December 2020.
Previous studies have reported slight increases in average weight / BMI (1.57kg / 0.31kg/m2) during the first three months of the pandemic. They also showed that weight / BMI changes in the early months were not uniform, with significant increases and decreases, and were associated with lifestyle, sociodemographic, and behavioral factors. However, due to the absence of longitudinal studies, it is largely unknown whether weight/BMI changes persist over longer durations and the factors linked to long-term weight/BMI changes.
.jpg)
A longitudinal study among UK adults using 3 surveys during May-December 2020
An online, longitudinal study conducted among 1,818 UK adults involved three surveys during May-June 2020, August-September 2020, and November-December 2020. The surveys covered weight, height, and sociodemographic, COVID-19-related interventions, and behavioral measures. The resulting data were analyzed with the help of generalized estimating equations. This study is available on the medRxiv* preprint server.
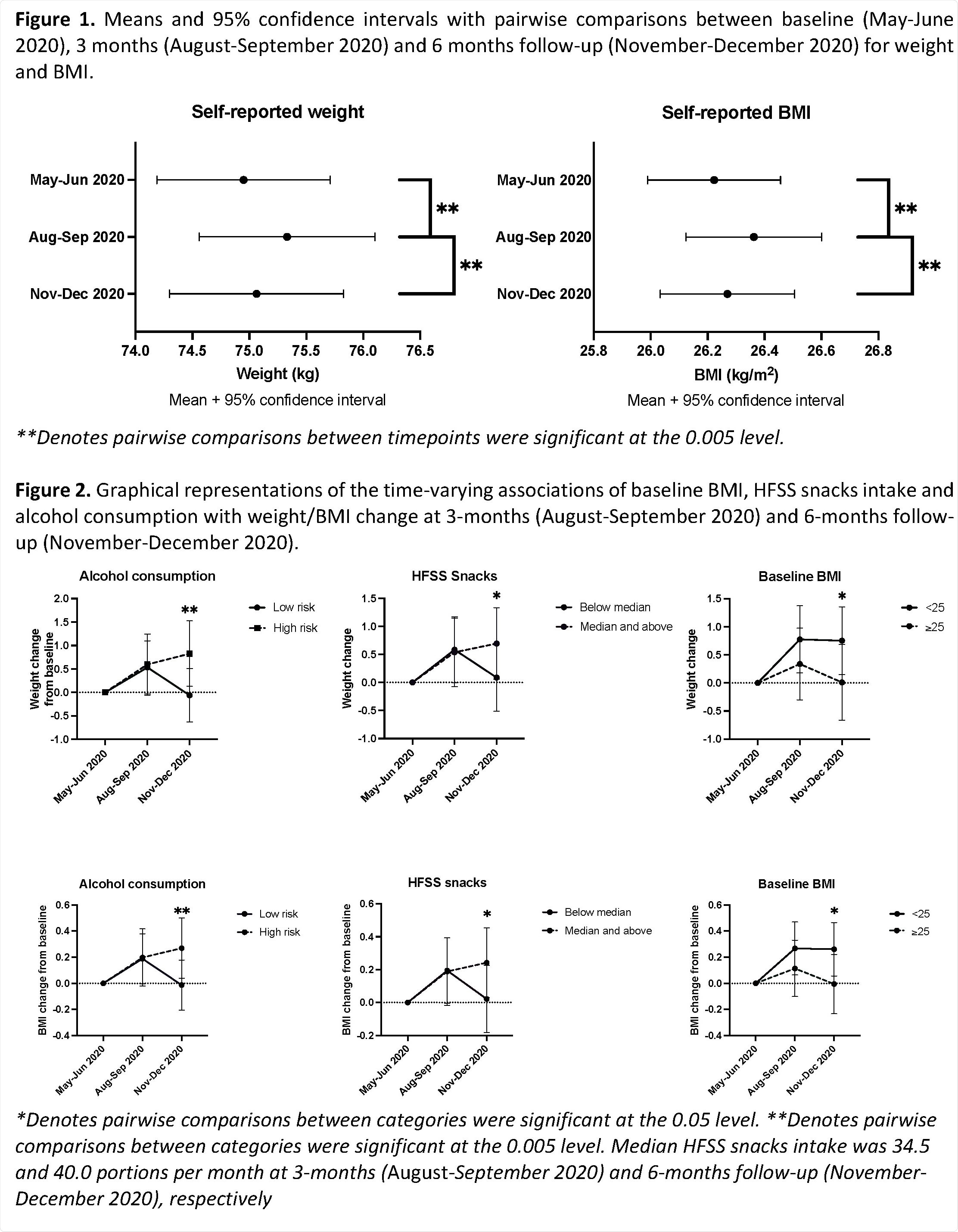
The results of the study showed that self-reported average weight (74.95kg to 75.33kg) and body mass index (BMI) (26.22kg/m2 to 26.36kg/m2) significantly increased from May-June 2020 to August-September 2020 and then considerably decreased to May-June levels of 75.06kg and 26.27kg/m2 in November-December.
However, there was a large inter-individual variation in weight/BMI from May-June to November-December. An increase in weight/BMI across surveys in fully adjusted models was significantly negatively linked to initial BMI and positively associated with high fat, salt, and sugar snacks intake and alcohol consumption.
“Older age was associated with an increase in BMI, and baseline BMI, and HFSS snacks intake and alcohol consumption showed timevarying associations with increasing both weight and BMI, primarily being associated with maintenance of initial weight gain in early 2020 through to the latter part of 2020.”
Results show that average weight / BMI first increased and then decreased In UK adults from May to December 2020
This study adds to previous works and reports that average weight / BMI first increased and then decreased in UK adults from May to December 2020. The findings also show that initial BMI and health behavioral factors including alcohol consumption, high fat, salt, and sugar intake at the start of the pandemic were significantly associated with weight/BMI changes.
“The strength of the association of alcohol consumption, initial BMI and HFSS snacks intake with weight/BMI change was dependent on the stage of the pandemic, with more pronounced differences becoming apparent during the latter part of 2020.”
Based on the findings, the average weight / BMI of UK adults part of the study increased during the early months of the pandemic, before decreasing to baseline levels in November-December 2020. However, this masks significant variation among individuals in weight / BMI trajectories, indicating vulnerabilities associated with food and alcohol consumption changes during the pandemic.
According to the authors, the results offer crucial details on the long-term health impacts of the pandemic on weight / BMI changes. This could help guide health policy and direct attention to the vulnerable population at an increased risk of poorer health outcomes due to weight gain.
Given that around two-thirds of UK adults were overweight and obese before the pandemic, the results of this longitudinal study showing an association between the pandemic and longer-term changes in weight / BMI are significant as they contribute to the existing obesity epidemic.
“Through self-reported survey data, this study in UK adults found a small, but significant increase in weight/BMI during the first three months of the pandemic, and a small, yet significant decrease in weight/BMI during the following three months.”
*Important Notice
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
- Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on weight and BMI among UK adults: a longitudinal analysis of data from the HEBECO study Samuel James Dicken, John Joseph Mitchell, Jessica Newberry Le Vay, Emma Beard, Dimitra Kale, Aleksandra Herbec, Lion Shahab medRxiv 2021.07.10.21259585; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.10.21259585, https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.07.10.21259585v1
Posted in:
Tags: Alcohol, Body Mass Index, Coronavirus Disease COVID-19, Mortality, Obesity, Pandemic, SARS-CoV-2

Written by
Susha Cheriyedath
Susha has a Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) degree in Chemistry and Master of Science (M.Sc) degree in Biochemistry from the University of Calicut, India. She always had a keen interest in medical and health science. As part of her masters degree, she specialized in Biochemistry, with an emphasis on Microbiology, Physiology, Biotechnology, and Nutrition. In her spare time, she loves to cook up a storm in the kitchen with her super-messy baking experiments.
Source: Read Full Article